Connect to WiFi
Materials
- Ameba x 1
Procedure
In the following, we will give a brief introduction on how to establish WiFi connection with these three types of encryption on Ameba.
First, make sure the current board is Ameba, select “Tools” -> “Board” -> “Arduino Ameba”.
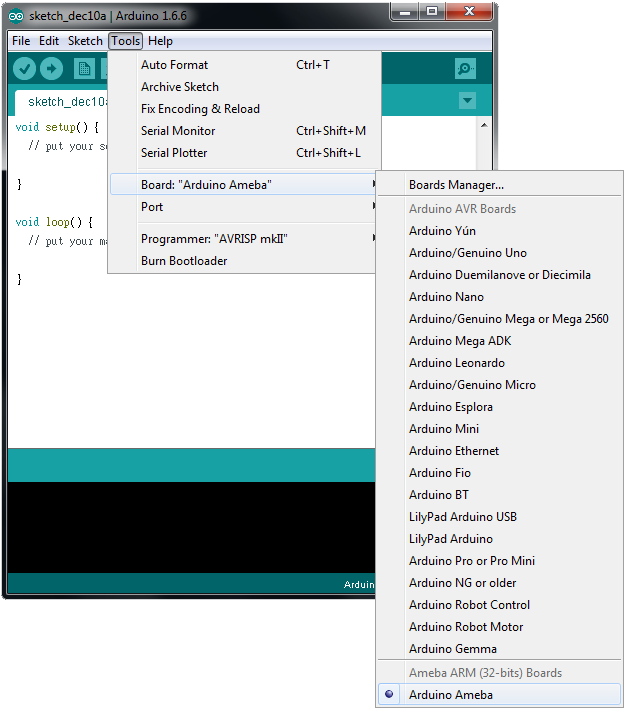
- Open (WiFi connection without password)
Open the “ConnectNoEncryption” example, “File” -> “Examples” -> “AmebaWiFi” -> “ConnectNoEncryption”
In the sample code, modify “SSID” to the SSID to be connected.
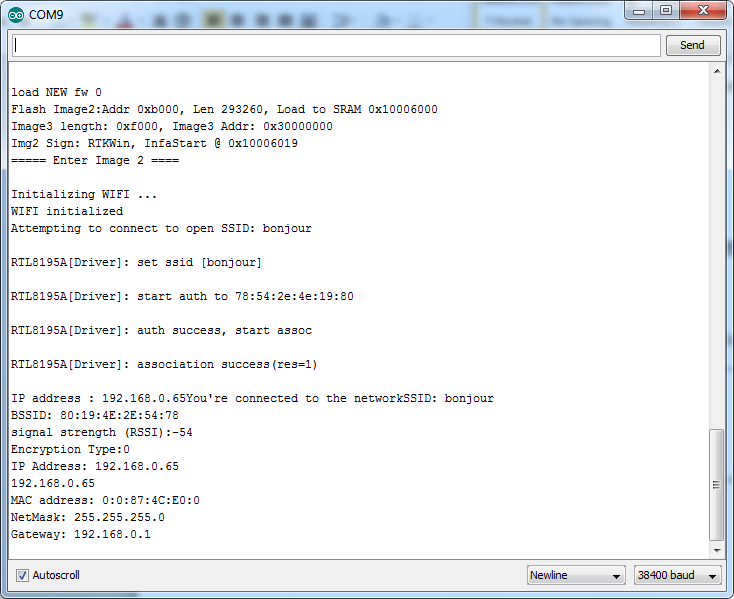
Next, upload the sample code, and press the reset button on Ameba. Then you will see a message says “You’re connected to the networkSSID: XXXXX”, and the information of this WiFi connection is printed in the IDE every 10 seconds.
- WiFi connection with WPA encryption
Open the “ConnectWithWPA” exmaple, “File” -> “Examples” -> “AmebaWiFi” -> “ConnectWithWPA”
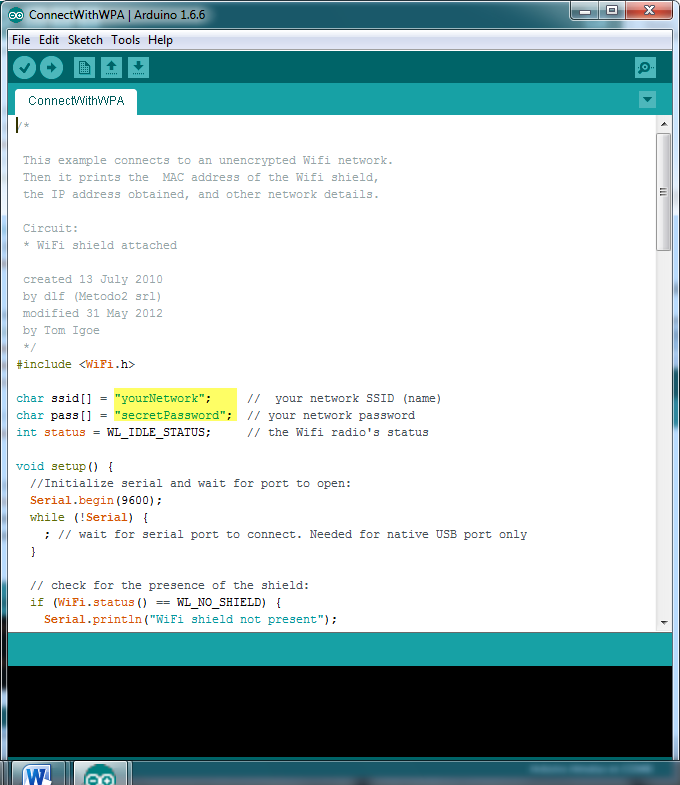
In the sample code, modify “SSID” to the SSID to be connected, “secretPassword” to be the password.
Next, upload the sample code, and press the reset button on Ameba. Then you will see a message says “You’re connected to the networkSSID: XXXXX”, and the information of this WiFi connection is printed in the IDE every 10 seconds.
- WiFi connection with WEP encryption
Open the “ConnectWithWEP” example, “File” -> “Examples” -> “AmebaWiFi” -> “ConnectWithWEP”
In the sample code, modify “SSID” to the SSID to be connected, “key” to the hexadecimal password, “keyIndex” to your key index number.
Code Reference
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiBegin
To get the information of a WiFi connection:
Use WiFi.SSID() to get SSID of the current connected network.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiSSID
Use WiFi.RSSI() to get the signal strength of the connection.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiRSSI
Use WiFi.encryptionType() to get the encryption type of the WiFi connection.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiEncryptionType
Use WiFi.BSSID() to get the MAC address of the router you are connected to.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiBSSID
To get the information of Ameba:
Use WiFi.macAddress() to get the MAC address of Ameba.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiMACAddress
Use WiFi.localIP() to get the IP address of Ameba.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiLocalIP
Use WiFi.subnetMask() to get the subnet mask.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiSubnetMask
Use WiFi.gatewayIP() to get the WiFi shield’s gateway IP address.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiGatewayIP
Comparison with Arduino
However, Ameba is already equipped with WiFi module. Therefore, #include is not needed.


